CustomTkinter
With CustomTkinter you can create modern looking user interfaces in python with tkinter. CustomTkinter is a tkinter extension which provides extra ui-elements like the CTkButton, which can be used like a normal tkinter.Button, but can be customized with a border and round edges.
CustomTkinter also supports a light and dark theme, which can either be set manually or get controlled by the system appearance mode.
Installation
To use CustomTkinter, just place the /customtkinter folder from this repository next to your program, or install the module with pip:
pip3 install customtkinter
Update existing installation: pip3 install customtkinter --upgrade
(from time to time bugs are getting fixed and new features are added)
PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/customtkinter/
Example program (simple button):
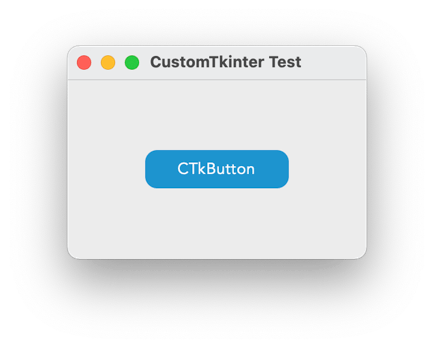
To test customtkinter you can try this simple example with only a single button:
import tkinter
import customtkinter # <- import the CustomTkinter module
root_tk = tkinter.Tk() # create the Tk window like you normally do
root_tk.geometry("400x240")
root_tk.title("CustomTkinter Test")
def button_function():
print("button pressed")
# Use CTkButton instead of tkinter Button
button = customtkinter.CTkButton(master=root_tk, corner_radius=10, command=button_function)
button.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
root_tk.mainloop()
which gives the following:
Use custom colors and shapes:
If you dont specify any colors, customtkinter uses the standard blue color in the light theme.
You can change the color theme to dark by calling
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("Dark").
If you specify custom colors for CustomTkinter elements, the you can either use a
tuple in the form: (light_color, dark_color). Or you can set a single color
which will be used in light and dark theme.
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("Dark") # Other: "Light", "System"
button = customtkinter.CTkButton(master=root_tk,
fg_color=("black", "lightgray"), # <- tuple color for light and dark theme
text="CTkButton",
command=button_event)
button.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
How to use macOS dark mode?
If you have a python version with Tcl/Tk >= 8.6.9, then you can enable the macOS darkmode. Currently only the anaconda python versions have Tcl/Tk >= 8.6.9. So if you want a dark window titlebar, you have to install anaconda python version or miniconda.
import tkinter
import customtkinter
customtkinter.enable_macos_darkmode()
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("System")
... the program ...
customtkinter.disable_macos_darkmode()
which gives the following with the above simple button program:
If you set the appearance mode to "System", it should change with the System mode:
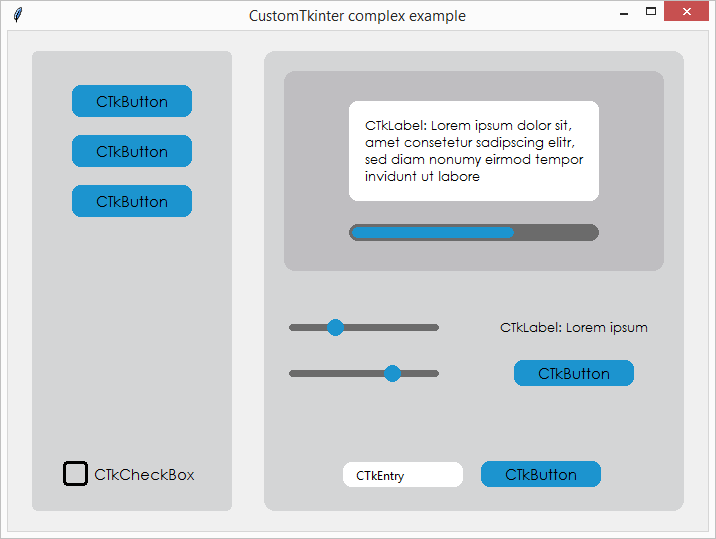
Advanced example with multiple CTkFrames
Here I used the customtkinter.enable_macos_darkmode() command to
enable the macOS darkmode, and used multpiple CTkFrames. It has some
kind of a menu on the left side, and I used all CustomTkinter elements
there are at the moment.Maybe this is a good reference if you want to
create your own application with this library.
(Code: /complex_example.py)
With macOS darkmode turned on, it looks like this:
Otherwise it looks like this:
But can also customize it by yourself. Here I changed the main colors and removed the round corners, and added a border to the buttons:
Customtkinter on Windows/Linux
All elements of Customtkinter are drawn on the tkinter.Canvas.
But the Tkinter canvas supports antialiasing only on macOS, so on Windows
and Linux the elements are rendered in a much worse quality. So you have
to experiment with the corner_radius and look when the rounded corners
look best. I tried to design the too complex example programs so that they
also look acceptable on Windows. Maybe you can use the parameters for
corner_radius and width for your program as well.
Example 1:examples/complex_example.py
Example 2: examples/complex_example_other_style.py
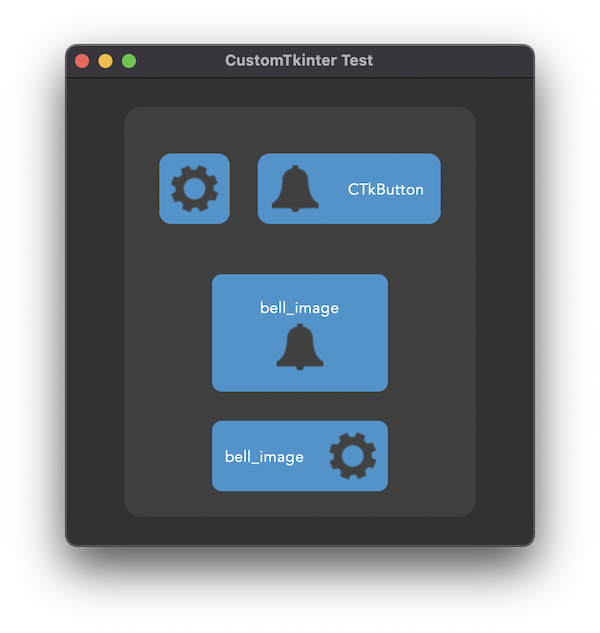
CTkButton with images
It's also possible to put an image on a CTkButton. You just have to
pass a PhotoImage object to the CTkButton with the argument image.
If you want no text at all you have to set text="" or with the compound
option you can specify how to position both the text and image at once.
You can find an example program ( /simple_test_images.py ), where I
created two buttons with a bell and a settings image on them:
Documentation - CustomTkinter Elements
CTkButton
Examle Code:
def button_event():
print("button pressed")
button = customtkinter.CTkButton(master=root_tk,
text="CTkButton",
command=button_event,
width=120,
height=32,
border_width=0,
corner_radius=8)
button.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| text | string |
| command | callback function |
| width | button width in px |
| height | button height in px |
| corner_radius | corner radius in px |
| border_width | button border width in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| border_color | border color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| hover_color | hover color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_color | text color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_font | button text font, tuple: (font_name, size) |
| hover | enable/disable hover effect: True, False |
| image | put an image on the button, removes the text, must be class PhotoImage |
| compound | set image orientation if image and text are given ("top", "left", "bottom", "right") |
| state | tkinter.NORMAL (standard) or tkinter.DISABLED (not clickable, darker color) |
CTkButton Methods:
CTkButton.set_text(new_text)
CTkButton.set_image(new_image)
CTkButton.configure(text=new_text)
CTkButton.configure(bg_color=new_bg_color,
fg_color=new_fg_color,
hover_color=new_hover_color,
text_color=new_text_color)
CTkButton.configure(state=tkinter.DISABLED)
CTkButton.configure(state=tkinter.NORMAL)
button_state = CTkButton.state
CTkLabel
Example Code:
label = customtkinter.CTkLabel(master=root_tk,
text="CTkLabel",
width=120,
height=25,
corner_radius=8)
label.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| text | string |
| width | label width in px |
| height | label height in px |
| corner_radius | corner radius in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color, None for transparent bg |
| text_color | label text color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_font | label text font, tuple: (font_name, size) |
CTkEntry
Example Code:
entry = customtkinter.CTkEntry(master=root_tk,
width=120,
height=25,
corner_radius=10)
entry.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
text = entry.get()
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| width | entry width in px |
| height | entry height in px |
| corner_radius | corner radius in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_color | entry text color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_font | entry text font, tuple: (font_name, size) |
CTkCheckBox
Examle Code:
checkbox = customtkinter.CTkCheckBox(master=root_tk,
text="CTkCheckBox")
checkbox.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| text | string |
| width | box width in px |
| height | box height in px |
| corner_radius | corner radius in px |
| border_width | box border width in px |
| fg_color | forground (inside) color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| border_color | border color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| hover_color | hover color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_color | text color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| text_font | button text font, tuple: (font_name, size) |
| hover | enable/disable hover effect: True, False |
| state | tkinter.NORMAL (standard) or tkinter.DISABLED (not clickable, darker color) |
CTkCheckBox Methods:
CTkCheckBox.get() # 1 or 0 (checked or not checked)
CTkCheckBox.select() # turns on checkbox
CTkCheckBox.deselect() # turns off checkbox
CTkCheckBox.toggle() # change check state of checkbox
CTkCheckBox.configure(text=new_text)
CTkCheckBox.configure(bg_color=new_bg_color,
fg_color=new_fg_color,
hover_color=new_hover_color,
text_color=new_text_color)
CTkCheckBox.configure(state=tkinter.DISABLED)
CTkCheckBox.configure(state=tkinter.NORMAL)
checkbox_state = CTkCheckBox.state
CTkSlider
Example Code:
def slider_event(value):
print(value)
slider = customtkinter.CTkSlider(master=root_tk,
width=160,
height=16,
border_width=5.5,
from_=0,
to=100,
command=slider_event)
slider.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| command | callback function, gest called when slider gets changed |
| width | slider width in px |
| height | slider height in px |
| from_ | lower slider value |
| to | upper slider value |
| border_width | space around the slider rail in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| border_color | slider border color, normally transparent (None) |
| button_color | color of the slider button, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| button_hover_color | hover color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
CTkProgressBar
Example Code:
progressbar = customtkinter.CTkProgressBar(master=root_tk,
width=160,
height=20,
border_width=5)
progressbar.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
progressbar.set(value)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| width | slider width in px |
| height | slider height in px |
| border_width | border width in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| border_color | slider border color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| progress_color | progress color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
CTkFrame
Example Code:
frame = customtkinter.CTkFrame(master=root_tk,
width=200,
height=200,
corner_radius=10)
frame.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor=tkinter.CENTER)
Show all arguments:
| argument | value |
|---|---|
| master | root, tkinter.Frame or CTkFrame |
| width | slider width in px |
| height | slider height in px |
| fg_color | forground color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
| bg_color | background color, tuple: (light_color, dark_color) or single color |
Special commands
Change appearance mode:
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("Light")
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("Dark")
customtkinter.set_appearance_mode("System")
print(customtkinter.get_appearance_mode())
Use macOS darkmode window style:
customtkinter.enable_macos_darkmode() # get darkmode window style
customtkinter.disable_macos_darkmode() # disable darkmode (important!)
If you dont use root_tk.mainloop(), then you have to deactivate
the threaded search for a change of the system appearance mode, and
do it yourself in your main loop where you call root_tk.update().
customtkinter.deactivate_threading() # call this at the beginning
customtkinter.update_appearance_mode() # then call this in the loop