5.2 KiB
Visual Studio Code Setup
Table of Contents
V language support
The V VS Code Extension provides V language support for Visual Studio Code.
Features:
- Syntax Highlighting.
- Code Snippets for quick coding.
- Format code on file save as well as format manually (using v fmt).
- Linter (Workspace files only). more
Hint: This extension will not add the V compiler! Information on how to install V compiler on your operating system.
Setup Extension
Install V VS Code Extension.
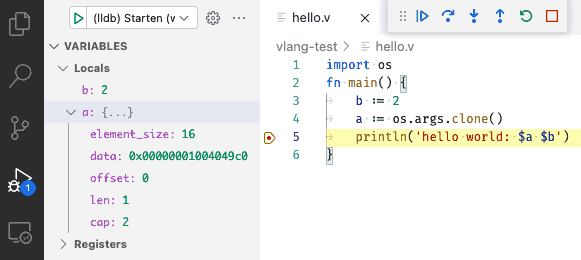
Visual Debugging
The C/C++ Extension for Visual Studio Code provides visual conditional debugging.
Features:
- Conditional breakpoints
- Function breakpoints
- Expression evaluation
- Change Values more Features & Documentation
Hint: Not all types (e.g. Array) in V currently create the required DWARF information to show and edit the variable.
Setup Debugging
Step1: Configure the launch.json file
- Install the C/C++ Extension
- Open
RUN AND DEBUGpanel (Debug Icon in left panel). - Click on
Showall automatic debug configurations. - Select
Add config. - Select environment
C++ (GDB/LLDB). - Change the line
"program": "Enter the program name, e.g. \"${workspaceFolder}/a.out\"",to point to your compiled application e.g."program": "${workspaceFolder}/hello",or a more flexible one"program": "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}",when you want to debug the current opened file.
This will add a block to your .workspace file,
or create the file .vscode/launch.json:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit:
// https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(lldb) Start",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "Enter the program name, e.g. \"${workspaceFolder}/a.out\"",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "lldb",
"preLaunchTask": "build"
}
]
}
Optional: use "program": "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}" to debug
any current open source file with an existing binary with the same name but without any extension.
Step2: Configure the tasks.json file
Generally, you can manually compile the application with: v -b c -g hello.v -o hello,
or for short: v -g hello.v, and then call the debugger.
The -g option will add the needed debugging information.
You can find more debugging options in the docs.
VS Code provides a hook called preLaunchTask, which can be used to compile
the application automatically every time you call the debugger.
preLaunchTask launches
a task before the start of a debug session, set this attribute to the label of a task specified
in task.json (in the workspace's .vscode folder).
Or, this can be set to ${defaultBuildTask}, to use your default build task.
As explained, the "preLaunchTask": "build" needs to work with a .vscode/tasks.json
with a label named build.
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "v",
"args": [
"-g", // add more compiler options here if necessary
"${relativeFile}" // or modify it according to your requirements
],
"group": "build",
"presentation": {
"reveal": "silent"
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}
Usage
To allow your compiled application to be debugged. The application needs to include additional debugging information (DWARF).
- Open your source code and set the required break points
- Click on the Debug Icon in the left Icon panel and click
> (lldb) Start, or useF5to launch your application in debug mode.
For all options look at the official C/C++ Extension documentation.